Searching via Box
Note: this article was originally posted on Box Support here and has been adapted for the use of UCLA HumTech.
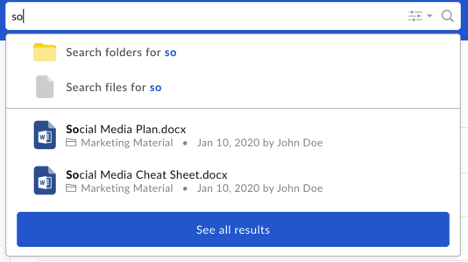
To search for a file or folder, click into the search bar shown in the center of the header. As you begin typing, suggested results will appear below the search bar. If one of the suggested results is the item you need, simply click on it to be taken to it directly. If you would like to see all the results for your search query or if you don’t see the file or folder you are looking for, press Enter/Return on your keyboard or click See all results at the bottom of the list of suggested results. Note: the order of results in the drop-down may vary from the full results page. Based on your enterprise settings, the results themselves may differ as well.
Using Search Filters:
Use filters to narrow down your search results:
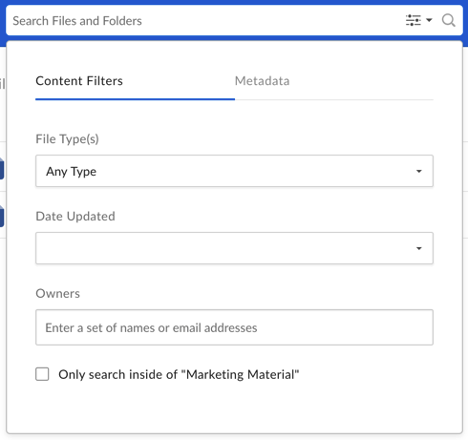
To open the filter menu, click the Search Options icon on the right side of the search bar. Under the Content Filters tab, you can filter results by file type, date modified, and file owner. Under the Metadata tab, you can filter results using custom metadata fields.
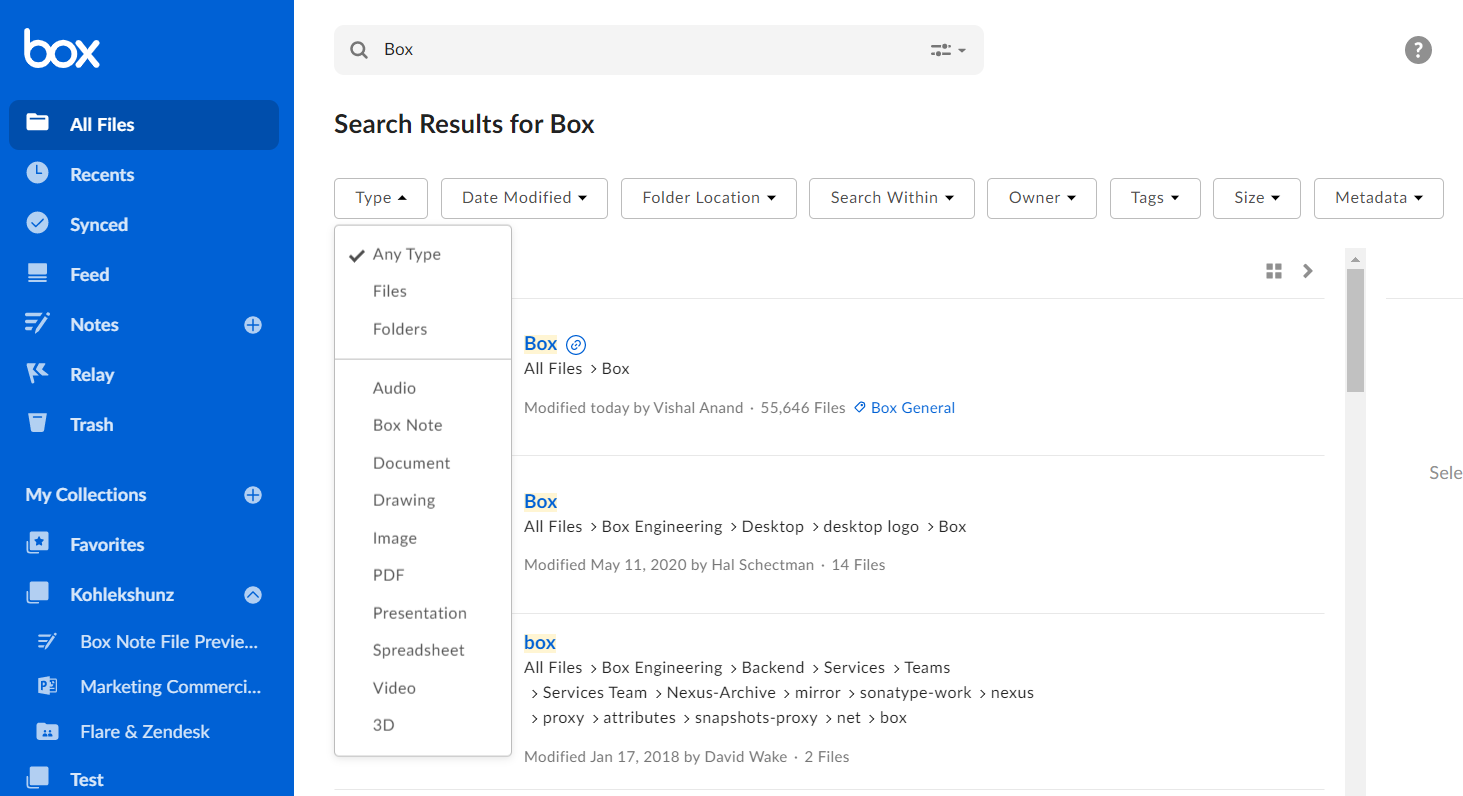
You can also set filters after viewing all search results from the search results page. Use the drop-downs at the top of the screen to filter by file type, file size, date modified, file owner, or custom metadata.
Exact Match
Use double quotes (“ “) to search for exact matches on phrases.
Note: Exact searches do not return search matches based on specific character sequences. Instead, they return matches based on phrases, that is, word sequences. For example: A search for "Blue-Box" may return search results including the sequence "blue.box", "Blue Box", and "Blue-Box"; any item containing the words "Blue" and "Box" consecutively.
Boolean Search
You can use Boolean operators in your search. The operators are AND, OR, and NOT. Please note that we do not support lower case (that is, "and", "or", and "not") or mixed case (that is, "And", "Or", and "Not") operators.
AND returns items that contain both the search terms. For example:
A search for marketing AND BoxWorks returns a result that has both marketing and BoxWorks within its text. It does not return a result that only has BoxWorks in its text.OR returns items that contain either of the search terms. For example:
A search for marketing OR BoxWorks returns a result that has either marketing or BoxWorks within its text. Using this operator is not necessary as we implicitly interpret multi-word queries as OR unless another supported Boolean term is used.NOT returns items that contain the first search term but not the second. For example:
A search for marketing NOT BoxWorks returns a result that has only marketing within its text. Results containing BoxWorks are omitted.
Long Queries
To preserve search performance, long queries (for example many words/tokens or many characters) may be truncated.
Saving Search Queries
After you initiate a search, the search query term and any filters are encoded as part of the URL – even the filters such as Date Modified are preserved.
This makes saving a search query much easier. The two options to save a query are via Box’s bookmark capability or via the browser’s bookmarking feature:
When you’ve conducted a search that you want to save, just copy the URL into the clipboard. Then navigate to the All Files page, click on + New in the header and then click on New Bookmark. In the address field paste the address that you copied from the search. Each time you click that link – the same search is executed!
You can also bookmark that URL using your browser – each time you visit that bookmark the search is executed.
How does search work?
Search Indexing
Box has a secure index for content much like the index in the back of a textbook. Every time a file or folder is changed, we add those words to the index in a process called indexing. When you conduct a search, we look in the search index for files and folders that match your query. When content is added, updated, or deleted in Box, we will update the search index accordingly.
Search Availability: It can take time between uploading or modifying a file for it to be fully indexed and ready to be searched. In most cases, you can expect newly added or changed files to be available via Box search in 10 minutes. The current service load determines the index time and it may take more than 10 minutes in some cases.
Search Access: Only content that you have access to (if you can preview and/or view) will display in search. Simply put, if you don’t have access to a file or folder within your account, it won’t show up in your search results. Files that you recently accessed via shared link can also appear in your search results.
Prefix Matching and Wildcard Search: Trailing wildcards (also known as prefix matching) are implicitly included in search results because of the way text is indexed. Searching for Bo results in items with titles containing Box or Boat or Boxer. It is the equivalent of searching for Bo* or Bo% in traditional search engines. Traditional wildcard notation is not supported by Box, such as %ox%. While we support prefix matching on titles, we do not support prefix matching on body content, suffix matching in the title or body content, or infix (middle of the word) matching in the title or body content. For example, a search on “cal” would match results for a file named “California” but not “decal” or “recall”. It would not match results with file body contents of prefixes, infixes, or suffixes including “California”, “recall”, or “decal”.
Stemming: Box Search uses stemming to match terms from the query to terms in the index. Because of this, words that include the same stem may be included in the result set, even if the words do not contain the exact form in the query. For example, “run” and “running” map to the same stem, so a search on “running” may return a document containing “run” in the title.
File Content Searching: The content within your files is also stored within the Box search index. The following file types support file content search: ‘boxnote’, 'csv', 'doc', 'docx', 'gdoc', 'gsheet', ‘gslide’, ‘gslides’, 'htm', 'html', 'msg', 'odp', 'odt', 'ods', 'pdf', 'ppt', 'pptx', 'rtf', 'tsv', 'wpd', 'xhtml', 'xls', 'xlsm', 'xlsx', 'xml', 'xsd', 'xsl', 'as', 'as3', 'asm', 'bat', 'c', 'cc', 'cmake', 'cpp', 'cs', 'css', 'cxx', 'diff', 'erb', 'groovy', 'h', 'haml', 'hh', 'java', 'js', ‘json’, 'less', ‘log’, 'm', 'make', ‘md’, 'ml', 'mm', 'php', 'pl', 'plist', 'properties', 'py', 'rb', ‘rst’, 'sass', 'scala', 'script', 'scm', 'sml', 'sql', 'sh', 'txt', 'vi', 'vim', 'webdoc', ’yaml’
Indexed Text per Document: The Box search index stores up to 10,000 bytes (~10,000 characters in English) per document for accounts from Business level and above. This amount can vary from document to document because of language, Box’s indexing method, and document type.
OCR Support: Box does not currently perform OCR on its documents.
Document Versions: Search only indexes content from the current version of a document, so that you do not have to sift through hundreds of irrelevant search results of outdated documents. You cannot use search to query non-current versions of a document.
Language Support: Box search supports the following languages: Chinese, English, French, German, Italian, Japanese, and Spanish. Box does not support indexing of multiple languages within a single document.
Trash: Searching the trash is available via the web and the API.
Search Relevance
The default order of the results displayed is based on the relevance score, which is our internal ranking system to predict with results are the most relevant for you based on your query.
Factors Considered for Relevance: We consider various factors in determining the order of results to show you. These include recency of the document, search query terms in the title, search query terms in the file contents and metadata (depending on account type and enterprise settings).
Continual Improvement: Search relevance is something that we are continuously working on improving. It is an iterative process and search relevance will improve over time. This means that result sets and ordering of results may change over time.
Individualized Results: You and your coworker may see different rankings for a variety of reasons such as you have access to different documents and you have varying personal histories in Box (for example, you have viewed/edited different files).
Sort by Date: If you prefer to see the results ordered by date updated, you can update the sort by drop-down to Updated.